Basics Of Communication System
- Data
– Information presented in whatever form is agreed upon by the parties creating and using the data
• Data communication
– Exchange of data between two devices
– Via some
form
of transmission medium
• Fundamental characteristics of
data
communication
– Delivery
– Accuracy
– Timeliness
• Telecommunication: communication at a distance
(‘tele’ in
Greek=‘far”)
Five Components of Data
Communication :
• Message:
Information (data) to be
communicated
• Sender
• Receiver
• Transmission medium: Physical path by which a
message travels
• Protocol: A set of rules that govern data communication
Transmission media is a pathway that carries the information from sender to receiver. We use different types of cables or waves to transmit data. Data is transmitted normally through electrical or electromagnetic signals.
An electrical signal is in the form of current. An electromagnetic signal is series of electromagnetic energy pulses at various frequencies. These signals can be transmitted through copper wires, optical fibers, atmosphere, water and vacuum Different Medias have different properties like bandwidth, delay, cost and ease of installation and maintenance. Transmission media is also called Communication channel.
Types of Transmission Media
1. Wired or Guided Media or Bound Transmission Media
2. Wireless or Unguided Media or Unbound Transmission Media
1) Wired or Guided Media or Bound Transmission Media: Bound transmission media are the cables that are tangible or have physical existence and are limited by the physical geography. Popular bound transmission media in use are twisted pair cable, co-axial cable and fiber optical cable. Each of them has its own characteristics like transmission speed, effect of noise, physical appearance, cost etc.
I) A Twisted Pair is a pair of copper wires, with diameters of 0.4-0.8 mm, twisted together and wrapped with a plastic coating. The twisting increases the electrical noise immunity, and reduces the bit error rate (BER) of the data transmission. A UTP cable contains from 2 to 4200 twisted pairs.
II) Coaxial Cable: Coaxial cable is a two-conductor cable in which one conductor forms an electromagnetic shield around the other. The two conductors are separated by insulation. It is a constant impedance transmission cable. This media is used in base band and broadband transmission. Coaxial cables do not produce external electric and magnetic fields and are not affected by them. This makes them ideally suited, although more expensive, for transmitting signals.
III) Optical Fiber : Optical fiber consists of thin glass fibers that can carry information at frequencies in the visible light spectrum and beyond. The typical optical fiber consists of a very narrow strand of glass called the core. Around the core is a concentric layer of glass called the cladding.
2) Wireless or Unguided Media or Unbound Transmission Media: Unbound transmission media are the ways of transmitting data without using any cables. These media are not bounded by physical geography. This type of transmission is called Wireless communication. Nowadays wireless communication is becoming popular. Wireless LANs are being installed in office and college campuses. This transmission uses Microwave, Radio wave, Infra red are some of popular unbound transmission media.
I) Radio Frequencies : The frequency spectrum operates from 0 Hz (DC) to gamma rays (1019 Hz). Radio frequencies are in the range of 300 kHz to 10 GHz. We are seeing an emerging technology called wireless LANs. Some use radio frequencies to connect the workstations together, some use infrared technology.
- Coves long distance.
- travels in any direction
- do not have to care about physical alignments of transmitter and reciver
-available in range 300KHz to 10GHz frequency
- radio waves communications affected by range ,sound, opstaclas like buildings etc.
-Used in arm forces ,police department
II) Microwave : Microwave transmission is line of sight transmission. The transmit station must be in visible contact with the receive station. This sets a limit on the distance between stations depending on the local geography. Typically the line of sight due to the Earth’s curvature is only 50 km to the horizon! Repeater stations must be placed so the data signal can hop, skip and jump across the country.
-Used for long distance up to 50KM
-After 50KM need repeaters towers Used in data communication in computer networks
-Transmission station must be in visible contact of receiving station.
III) Satellite : Satellites are transponders (units that receive on one frequency and retransmit on another) that are set in geostationary orbits directly over the equator. These geostationary orbits are 36,000 km from the Earth’s surface. At this point, the gravitational pull of the Earth and the centrifugal force of Earth’s rotation are balanced and cancel each other out. Centrifugal force is the rotational force placed on the satellite that wants to fling it out into space.
-Satellite is artificial space scraft place in a orbit (36000KM)from each having transponders receive signal from earth station and send signals to earth from satellite dish antennas satellite station.
-Covers world wide area -Microwaves between 12GHz to 14GHz used.
IV)Infrared signals can be used for short-range communication in a closed area using line- of-sight propagation.
- Infrared waves with frequencies from 300 GHz to 400 THz for short-range communication in a closed area using line-of-sight propagation
• Having high frequencies, it cannot penetrate walls
• IrDA (Infrared Data Association) for standards
• Example: IrDA port for wireless keyboard
– Originally defined a data rate of 75 kbps for a distance up to 8 m
– Recent standard for a data rate of
4 Mbps
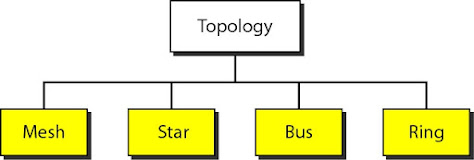
Network Topology
Types of Networks
• Usually privately owned
• A network for a
single office, building, or campus a few Km
• Common
LAN
topologies: bus, ring, star
• An isolated LAN connecting 12
computers to a hub in a closet
2) MAN -( Metropolitan Area Network)
• Designed to extend to
an entire city
• Cable TV network, a company’s connected LANs
• Owned by a private or a public company
• Long distance transmission, e.g., a country, a continent, the world
• Enterprise network: A WAN that is owned and used by one company