Data dictionary
A data dictionary contains metadata i.e data about the database. The data dictionary is very important as it contains information such as what is in the database, who is allowed to access it, where is the database physically stored etc. The users of the database normally don't interact with the data dictionary, it is only handled by the database administrators.
The data dictionary in general contains information about the following −
- Names of all the database tables and their schemas.
- Details about all the tables in the database, such as their owners, their security constraints, when they were created etc.
- Physical information about the tables such as where they are stored and how.
- Table constraints such as primary key attributes, foreign key information etc.
- Information about the database views that are visible.
This is a data dictionary describing a table that contains employee details.
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Size for display | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employee Number | Integer | 10 | Unique ID of each employee | 1645011001 |
| Name | Text | 20 | Name of the employee | M.K Rao |
| Date of Birth | Date/Time | 10 | DOB of Employee | 08/03/1994 |
| Phone Number | Integer | 10 | Phone number of employee | 6083648648 |
The different types of data dictionary are −
Active Data Dictionary
If the structure of the database or its specifications change at any point of time, it should be reflected in the data dictionary. This is the responsibility of the database management system in which the data dictionary resides.
So, the data dictionary is automatically updated by the database management system when any changes are made in the database. This is known as an active data dictionary as it is self updating.
Passive Data Dictionary
This is not as useful or easy to handle as an active data dictionary. A passive data dictionary is maintained separately to the database whose contents are stored in the dictionary. That means that if the database is modified the database dictionary is not automatically updated as in the case of Active Data Dictionary.
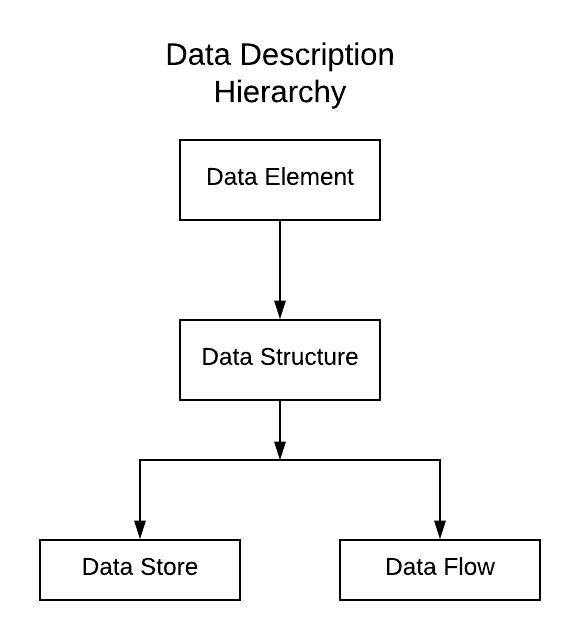
Components of Data Dictionary
There are basically three components of data dictionary:
- Data Element
- Data Structure
- Data Flows & Data Store
1. Data Element
Data element is the smallest unit of data that has some meaning. It cannot be decomposed further.
For example
Employee number, age of employee, quantity ordered etc.
2. Data Structure
Data structure is a group of data elements that describe a unit in the system.
For example
BOOK DETAILS consisting of the data elements author name, title, ISBN, price, publisher’s name & address.
3. Data Flows and Data Stores
Data Flows are data structures in motion where as data stores are data structures at rest. Data stores may be files, database etc.
Advantages of Data Dictionary
- It is a valuable reference for designing the system
- It facilitated analysis in determining additions & modifications in the system
- It is used to locate errors in the system descriptions
- It helps the analyst to record the details of each element and data structure
- It helps in communicating meanings of different elements, terms & procedures.
